Amplifying Analog Voltages with the LM358
05.03.2025
Elektronik | Funk | Software
Der Technik-Blog

There is also a video on YouTube for this article: Capacitive sensors - basics and how to use the proximity sensors with Arduino
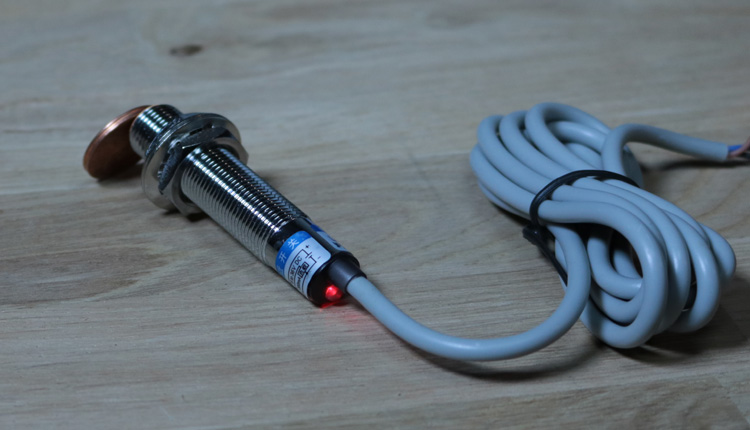
A capacitive sensor or proximity sensor detects capacities changes in the environment. The sensor reacts on various materials that have a certain conductivity. These mainly include metals and liquids. Some sensors also have the possibility to adjust the sensitivity. This can be done via a potentiometer or a button, with it the sensor can be teached to the capacity of the environment. The sensor comes from the industry, which therefore the most sensors work with 24 volts. The sensor is often used to detect filling levels in tanks, air bubbles in pipes or for detecting leaks. In addition, it can also be used as a metal detector, touch sensor or as a door contact.
The sensor is also perfect useful for many Arduino projects. Some sensors are working in a wide voltage range from 6 to 36 volts. It will also work with 5 volts on the Arduino. In this case, you can use simply the supply voltage from the Arduino board and connect the signal line to a digital input on controller. The Arduino read the defined digital input pin and get the status of the sensor (HIGH or LOW).
Many sensors only work with 24 volts. So that sensors with a switching level of more than 5 volts also work on the Arduino, a corresponding voltage divider must be built. The simple voltage divider have two resistors that convert the 24 volts to 5 volts. In this example we use a series connection of a 1800 ohm and a 470 ohm resistor. In the middle of the circuit we connect the digital pin of the Arduino.
The example code is relatively simple and works like the example code of a button. First the digital input pin is defined. In the main loop, the digital pin is queried and, depending on the status (0 or 1), the corresponding output takes place in the Serial Monitor. It will then indicate if the sensor is active or not.
int sensorpin = 2;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(sensorpin, INPUT);
}
void loop() {
int sensorstate = digitalRead(sensorpin);
if (sensorstate == 1) {
Serial.println("Cap. Sensor active");
} else {
Serial.println("Cap. Sensor not active");
}
delay(10);
}
On this page we will show you how to make a data transfer with the CC1101 and an Arduino. Wiring plan and libraries are available on AEQ-WEB
read more
Fans in PCs and industrial equipment have a tachometer signal line. This article is about the speed measurement of a fan with an Arduino
read moreAEQ-WEB © 2015-2026 All Right Reserved