Amplifying Analog Voltages with the LM358
05.03.2025
Elektronik | Funk | Software
Der Technik-Blog

A central component of LoRaWAN is the Device Address (DevAddr). Each end device has a Device Address, which is either statically assigned (ABP) or allocated to the end device by the respective LoRaWAN network server during the JOIN request (OTAA). The Device Address is used to identify and manage devices within a LoRaWAN network. This article takes a closer look at the structure, function, and significance of the DevAddr in LoRaWAN and explains why it is important for users, developers, and network operators.
The assignment of the Device Address (DevAddr) depends on the activation mode of the LoRaWAN end device. There are two methods by which an end device receives a DevAddr:
Activation by Personalization (ABP):
With ABP, the DevAddr is directly set in the end device before it communicates with the network. This offers the advantage of immediate readiness but lacks the ability to dynamically respond to network conditions, as there is no interaction with the network server. In ABP, the Device Address is usually programmed into the end device by the manufacturer.
Over-the-Air Activation (OTAA):
OTAA is the preferred method for dynamic and secure LoRaWAN implementations. In this case, the DevAddr is generated by the LoRaWAN network server during the JOIN process and assigned to the end device.
The Device Address is 4 bytes or 32 bits in size and consists of two parts. The first part is the network identification (NetID), and the second part is the device address (NetAddr):
The NetID consists of a type prefix and the actual NetID. The type prefix is 3 bits in size and indicates, in decimal values from 0 to 7, the maximum number of end devices per address range. The size of an address range is allocated by the LoRa Alliance and depends on the type of membership. Large sponsors and developers are assigned a Type 0 and Type 3 address range (e.g., Swisscom or TTN), while large companies and contributor members receive a Type 3 and Type 6 address range. Companies that do not contribute to development or only offer services as LoRaWAN network operators are assigned a Type 6 address range. The following graphic illustrates the sizes of the address ranges:
The following graphic illustrates the structure of a Device Address with a 7-bit, 15-bit, and 22-bit NetID. TTN is a global network and therefore assigns end devices exclusively a Device Address with a 7-bit NetID!
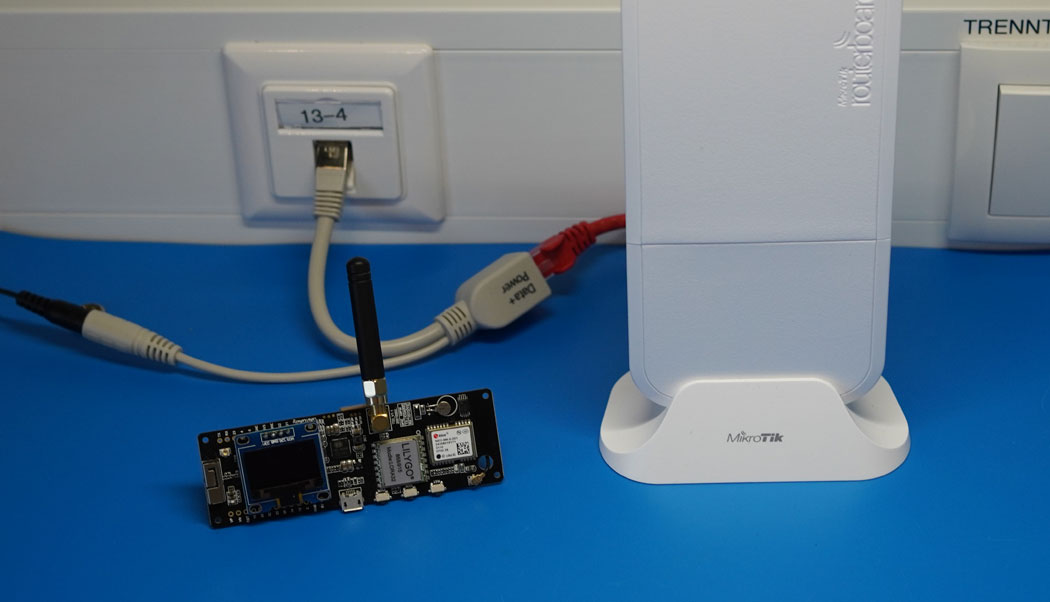

The UDP packet forwarder developed by Semtech handles the data transmission of the received packets from the LoRaWAN gateway to the network server
read more
The ESP32 LoRa board from Heltec supports LoRa. This article is about access and data transfer to LoRaWAN & TTN
read moreAEQ-WEB © 2015-2025 All Right Reserved