Daly BMS Fernauslesen mit LoRaWAN
05.12.2025
Elektronik | Funk | Software
Der Technik-Blog
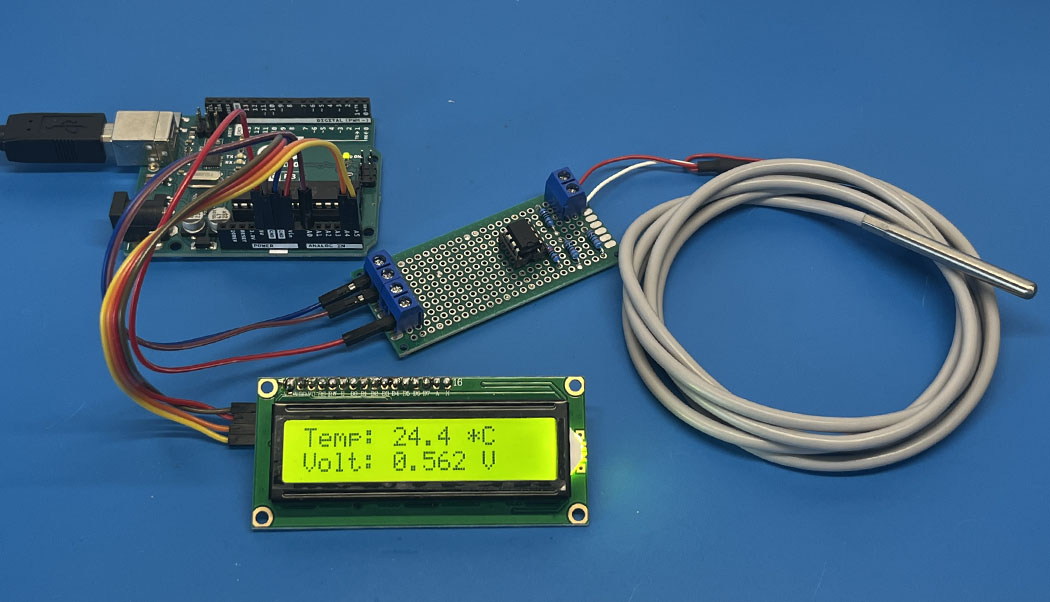
Beispielcode vom Projekt PT100 Temperatur messen mit dem Arduino. Dieser Beispielcode gibt die gemessenen Temperaturwerte im Serial Monitor und auf einem 16x2 I2C LC-Display aus.
//More information about this project can be find here: https://www.aeq-web.com/pt100-temperature-sensor-arduino-r-u-converter/ #include <SoftwareSerial.h> #include <Wire.h> #include <LiquidCrystal_I2C.h> LiquidCrystal_I2C lcd(0x27, 16, 2); // set the LCD address to 0x27 for a 16 chars and 2 line display const int pt100Pin = A0; // Define PT100 input pin const float offset = -0.00; // Offset (depending on the line resistance) // Define known points (voltage & temperature) const float voltages[] = { 0.079, 0.56, 1.04, 1.99, 2.95 }; // Voltages in Volts const float temperatures[] = { 0, 25.0, 50.0, 100.0, 150.0 }; // Temperatures in Celsius const int numPoints = sizeof(voltages) / sizeof(voltages[0]); // Linear interpolation float interpolate(float x, float x0, float x1, float y0, float y1) { return y0 + (y1 - y0) * (x - x0) / (x1 - x0); } // Calculate temperature from voltage float calculateTemperature(float voltage) { // Set to 0°C if voltage is higher than max. known point if (voltage > voltages[numPoints - 1]) { return 999; } // Find limits for interpolation int i = 0; while (voltage > voltages[i + 1] && i < numPoints - 1) { i++; } // Interpolate between limits return interpolate(voltage, voltages[i], voltages[i + 1], temperatures[i], temperatures[i + 1]); } void setup() { Serial.begin(9600); lcd.init(); // Print a message to the LCD. lcd.backlight(); lcd.setCursor(2, 0); lcd.print("PT100 Tester"); lcd.setCursor(0, 1); lcd.print("WWW.AEQ-WEB.COM"); delay(5000); lcd.clear(); } void loop() { int sensorValue = analogRead(pt100Pin); float voltage = sensorValue * (5.0 / 1023.0); float temperature = calculateTemperature(voltage)+offset; lcd.clear(); Serial.print("Voltage: "); Serial.print(voltage, 3); Serial.print("V, Temperature: "); Serial.print(temperature, 1); Serial.println("°C"); lcd.setCursor(0, 0); lcd.print("Temp: "); lcd.print(temperature, 1); lcd.print(" *C"); lcd.setCursor(0, 1); lcd.print("Volt: "); lcd.print(voltage, 3); lcd.print(" V"); delay(1000); }

LoWTRACK ist eine App für LoRaWAN GPS-Tracker. LoWTRACK zeigt Positionsdaten, Gateway-Details und viele Informationen über das verbundene LoRaWAN-Netzwerk an.
Weiterlesen
Täglich fallen Hunderte meteorologische Radiosonden vom Himmel. In diesem Artikel bauen wir eine Radiosonde zu einen GPS-Tracker für APRS, RTTY & CW um
WeiterlesenAEQ-WEB © 2015-2025 All Right Reserved